Bellman-Ford Algorithm
The Bellman-Ford Algorithm finds shortest paths from a given source to all vertices of the graph. Unlike Dijkstra’s Algorithm, it works well even for the graphs having negative weight edges.
Time Complexity: O(|V||E|).
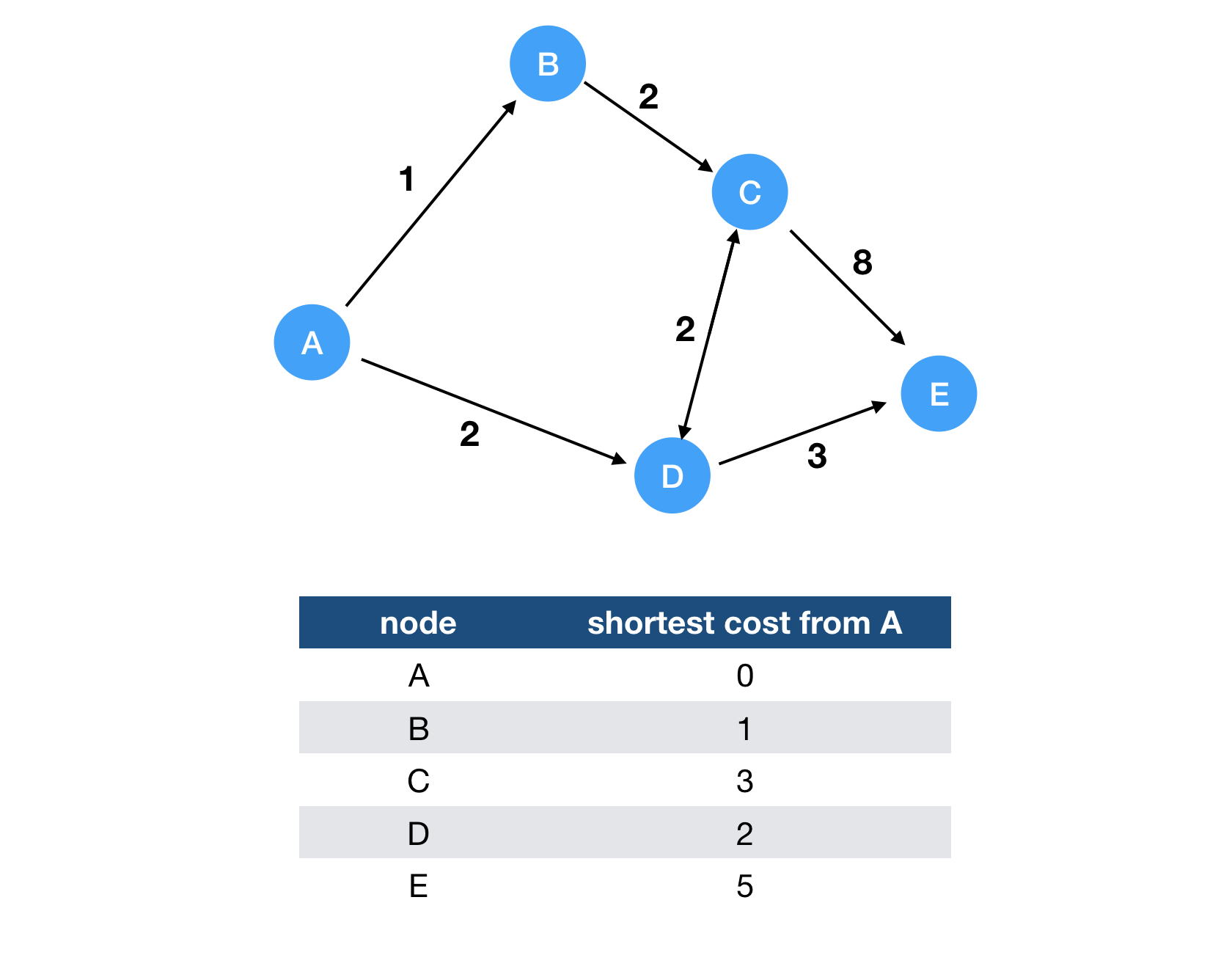
Application: This algorithm can be used for detecting negative weight cycle in the graph regardless of the src node.
Note: If the graph contains a negative weight cycle, shortest path for any vertex that contains the cycle looses its meaning as we can shorten path length as many times as we want by repeating the cycle again and again.
Pseudo code for Bellman-Ford Algorithm:
BellmanFord(Graph,src)
{
distance[V] = {INF}; # initialize the distance for every vertex with Infinity.
distance[src] = 0;
for i = 1 to i = n-1 :
for every edge e in Graph: # e = (u,v,w) => there is an edge between u and v with weight w.
distance[e.v] = min(distance[e.v],distance[e.u] + e.w);
# by now, all the distances have been minimized but if we still get any shorter path in this iteration,
# that means there is a negative weight cycle in the graph.
for every edge e in Graph:
if(distance[e.v] > distance[e.u] + e.w):
print("Graph contains a negative weight cycle")
break;
}References: GeeksforGeeks, MIT video lecture